Whenever a large truck roars past, people will always hear a low rumbling sound and feel the house shaking. This is because the weight of heavy vehicles will make the road slightly sag, and it will also affect the overall fuel efficiency of the truck. .
(Photo source: MIT)
Now, according to foreign media reports, a theoretical study conducted by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has shown that a slight change in road paving can reduce the loss of vehicle fuel efficiency, and the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions in the transportation field can be reduced with little cost. Reduce by 0.5%.
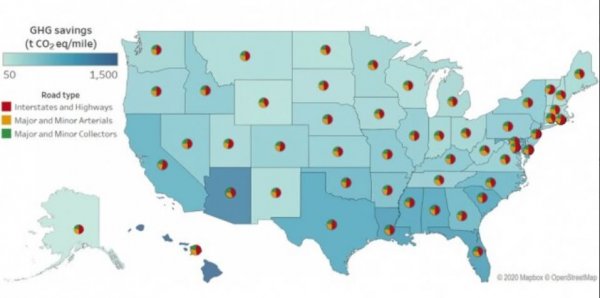
The study investigated data on weather conditions, road lengths, material characteristics, and road usage in various states of the United States, and established models for different pavement re-laying schemes. The researchers found that one of the keys to improving mileage efficiency is to make the road harder to reduce the degree of road surface deflection, thereby reducing road wear and also reducing the slight uphill movements that vehicles constantly make to get rid of road depressions.
Researchers say there are predictions that the number of passenger car trips will decrease slightly in the future, but truck freight trips will increase, and road deflection will affect their overall efficiency.
However, researchers say there are several ways to make the road harder. One is to add a small amount of synthetic fibers or carbon nanotubes to the asphalt mixture when laying asphalt. Only one-tenth of such cheap materials can greatly improve the hardness of the road. Another way to increase the hardness is to adjust the particle size of aggregates of different sizes in the asphalt mixture, increase the amount of rock, reduce the amount of binder, and make the mixture more dense.
Another method is to replace the asphalt pavement with a concrete pavement. The latter has a higher initial cost, but is more durable, so the total life cycle cost is the same or lower than the asphalt pavement. Concrete is already used on pavements in many states in the northern United States, and asphalt is more popular in southern states. Because asphalt is particularly susceptible to deformation under hot weather conditions, and concrete roads are relatively unaffected by high temperatures, roads in southern states have a greater impact on vehicles. Studies have shown that simply upgrading the pavement in Texas has had a major impact, because the state has a huge asphalt road network and high temperature weather.
The researchers calculated that the road improvement rate of only 10% can reduce 440 million tons of carbon dioxide emissions within 50 years, accounting for about 0.5% of the total traffic-related emissions during this period. However, this proposal may bring some adjustments, because changing the asphalt mixture may affect the operation of the field work, and the equipment used may need to be adjusted. There may also be some processing costs. (Yu Qiuyun)
Sheet Metal Chassis And Cabinet
Suzhou Green New Material Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.glooptube.com