Foreword
5.1, 5.2.1, 5.2.2, and 5.3 of this standard are mandatory, and the rest are recommended.
This standard was proposed by the China National Light Industry Council.
This standard is standardized by the National Lighting Standardization Technical Committee (SAC/TC 224).
This standard was drafted by: Huangming Solar Energy Group Co., Ltd., Yingli Energy (Beijing) Co., Ltd., Zhejiang Sunshine Group Co., Ltd., Shandong Shengyang Power Supply Co., Ltd., Foshan Huaquan Electric Lighting Co., Ltd., and Zhonghai Yang (Beijing) Co., Ltd. Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Liangye Lighting Engineering Co., Ltd., Zhongdian Electric (Nanjing) Solar Energy Research Institute Co., Ltd., Beijing Zhongan Infinity Technology Co., Ltd., Zhongshan Yuzhiyuan Solar Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Jiangxi Guiya Green Lighting Co., Ltd., Guangzhou New Style Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Tongxiang Shenghui Lighting Appliance Co., Ltd., Beijing Changri New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing Tianyun Solar Energy Technology Development Co., Ltd., Zhangjiakou Baosheng New Energy Technology Co., Ltd., and Beijing Sunsail Technology Development Co., Ltd. Beijing Lighting Society.
The main drafters of this standard: Wang Jianning, Zhao Jianping, Wu Guoming, Kong Delong, Di Zhiyang, Xue Liming, Li Fumin, Jia Yangang, Lin Qinghong, Lei Zongping, Pan Xiaoping, Li Chunhai, Shen Jinxiang, Cao Chunfeng, Fang Fengjie, Lu Jianxiang, Meng Xiangwu, Ke Baiquan, Tu Daoping, and Wang Dayou.
1 Scope
This standard specifies the scope, equipment and classification, device requirements, component requirements, test methods, and acceptance rules for solar photovoltaic lighting devices.
This standard applies to solar photovoltaic lighting devices in roads, public places, gardens, advertising, signs and decorations and other lighting places.
2 normative references
The clauses in the following documents have been adopted as references to this standard. For dated references, all subsequent amendments (not including errata content) or revisions do not apply to this standard, however, encourage the parties to reach an agreement based on this standard to study whether the latest version of these documents can be used . For undated references, the latest version is applicable to this standard.
GB/T 191 packaging, storage and transportation logo (GB/T 191-2008, ISO 780:1997, MOD)
GB/T 2828.1 Count Sampling Inspection Procedures Part 1: Batch Inspection Sampling Plans Retrieved by Acceptance Quality Limit (AQL) (GB/T 2828.1-2003, ISO 2859-1:1999, IDT)
GB/T 2829 periodic inspection count sampling procedure and table (applicable to process stability test)
GB 7000.1 luminaires Part 1: General requirements and tests (GB 7000.1-2007, IEC 60598-1:2003, IDT)
GB 7000.5 Road lighting and street lighting safety requirements (GB 7000.5-2005, IEC 60598-2-3:2002, IDT)
GB/T 9468 Luminaire Distribution Photometric Measurement General Requirements
GB/T 9535 surface crystalline silicon photovoltaic module design identification and stereotypes (GB/T 9535-1998, eqv IEC 1215:1993)
GB/T 11011 General rules for testing the electrical properties of amorphous silicon solar cells
Performance requirements for AC electronic ballasts for GB/T 15144 tubular fluorescent lamps (GB/T 15144-2009, IEC 60929:2006, MOD)
GB/T 18911 ground-based thin-film PV module design qualification and finalization (GB/T 18911-2002, IEC 61646: 1996, IDT)
GB/T 19064-2003 Technical requirements and test methods for domestic solar photovoltaic power systems
GB 19510.1 lamp control device Part 1: General requirements and safety requirements (GB 19510.1-2009, IEC 61347-1:2007, IDT)
GB 19510.5 Lamp control apparatus Part 5: Particular requirements for dc electronic ballasts for general lighting (GB 19510.5-2005, IEC 61347-2-4:2000, IDT)
GB/T 19638.2 fixed valve-regulated lead-acid batteries
GB/T 19639.1 small valve-regulated lead-acid battery technical conditions
Performance requirements for GB/T 19656 DC electronic ballasts for tubular fluorescent lamps (GB/T 19656-2005, IEC 60925:2001, IDT)
3 Terms and Definitions
The following terms and definitions apply to this standard.
3.1
Solar photovoltaic lighting equipment solar photovoltaic (PV) lighting installation
A solar device, a battery, a lighting component, a controller, and a mechanical structure are combined to use solar energy as an energy source, and an off-grid, independent-use lighting device comprising one or more groups of lamps.
3.2
Solar cell module solar cellmodule
With a package and internal connection, can be independently provided with direct current output, the smallest integral solar cell combination device.
3.3
Charge and discharge controller charge and discharge controllers
It has a control device that automatically controls the solar battery module to charge the battery and the battery discharges to the lighting part.
3.4
Inverter
A conversion device that converts direct current to single-phase alternating current with a voltage of 220 V, a frequency of 50 Hz, and a voltage waveform of a sine wave or quasi-sine wave.
3.5
Luminaire efficiency
Under the same conditions of use, the ratio of the total luminous flux emitted by the lamp to the total luminous flux emitted by all the light sources in the lamp.
3.6
Semi-cut-off luminaire
The luminaires with the maximum light intensity and the maximum allowable value of the light intensity at the downward vertical axis angle of the light fixture between 0°-75°, 90° angle and 80° angle are 50cd/1000lm and 100cd/1000lm, respectively. And regardless of the size of the light flux of the light source, the maximum intensity of the light at the 90° angle should not exceed 1000 cd.
3.7
Lamp installation height luminairemounting height
The vertical distance from the light center of the lamp to the road surface.
4 Devices and Classification
4.1 Device
The device consists of the following components:
a) Solar photovoltaic conversion component (solar cell assembly);
b) Energy storage components (battery and other storage energy devices);
c) Control components (charge and discharge controllers, inverters);
d) lighting components (electrical light sources and their accessories and luminaires);
e) structural components (poles, solar cell module holders, battery chambers and controller rooms, etc.);
f) Charge and discharge lines.
4.2 Device Classification by Use and Use
4.2.1 Solar lights for solar photovoltaic lighting: lighting for public places, courtyards, residential areas, leisure areas, and pedestrian roads.
4.2.2 Street lighting for solar photovoltaic lighting: road lighting.
4.2.3 Decorative lighting for solar photovoltaic lighting: Night landscape lighting.
4.2.4 Light boxes for solar photovoltaic lighting: advertising, signage lighting.
5 device overall requirements
5.1 Operating Environment
5.1.1 The device shall be able to work normally within the ambient temperature range of -20°C to 50°C (manufactures can adjust the lower temperature limit according to the application area requirements).
5.1.2 The device application can provide normal illumination in the continuous 2-n shade, rain, and snow days (the manufacturer adjusts the upper limit n according to the conditions of the application area).
5.1.3 The device should not be installed in places with tall buildings and trees blocking the sunlight-exposed surface of solar panels.
5.2 General requirements
5.2.1 The electric light source shall be turned on and off automatically according to the ground illumination value or at the set time (as required by the manufacturer according to the application area).
5.2.2 device performance:
a) Electrical efficiency: The ratio of the lighting component power to the battery's rated output power should be greater than 90%;
b) Continuous discharge capability: Maintain normal lighting as required by 5.1.2. On the last day, the battery should have at least 20% of the remaining power.
5.2.3 The electric light source should be selected according to the different needs of different places. The available electric light sources are:
Double-end fluorescent lamps, single-end fluorescent lamps, electrodeless fluorescent lamps, high-intensity discharge lamps, low-pressure sodium lamps, light emitting diodes (LEDs) and other electric light sources.
Low-pressure sodium lamps are only suitable for road lighting.
5.3 Safety Requirements
5.3.1 The device shall have sufficient strength to withstand 10 wind loads (the manufacturer shall adjust the wind load level according to the conditions of the application area).
5.3.2 Device protection rating should be greater than IP54.
5.3.3 The advertising light box and the lamp pole above 4m should have good lightning protection grounding, and the grounding resistance should be less than 30Ω.
5.3.4 The insulation resistance between the live body and the device metal parts should be greater than 2MΩ.
5.3.5 The controller room and battery room shall have good waterproofing measures to prevent battery pollution.
5.3.6 Dedicated tools should be used for disassembly.
6 device parts requirements
6.1 Solar Photoelectric Conversion Unit
6.1.1 The technical performance of crystalline silicon solar cell modules shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 9535.
The technical performance of amorphous silicon and other thin film solar modules should meet the requirements of GB/T 11011 and GB/T 18911.
6.1.2 The power of the solar cell module square shall be determined according to the conditions of use, lighting resources and load, and shall meet the total power consumed by lighting components, control components, energy storage time and charge and discharge lines.
6.1.3 Regardless of the charging control method used, the working voltage of the solar module should meet the requirements of the battery charging voltage.
6.1.4 solar module square array should have a self-cleaning ability.
6.2 Energy storage components
Should choose valve-regulated lead-acid batteries, its performance should be consistent with the provisions of GB/T 19638.2 or GB/T 19639.1.
Select other types of energy storage components, its performance should meet or better than the relevant provisions of GB/T 19638.2 or GB/T 19639.1.
6.3 Control Units
6.3.1 The performance of the charge-discharge controller shall comply with the requirements of 6.3.2-6.3.13 and related standards in GB/T 19064-2003.
6.3.2 Switch Light Control Methods and Requirements
a) It is advisable to use light control, time control or a combination of both;
b) The timing of opening and closing lights should be adjustable, and the time error when turning lights on and off should not exceed 1 min.
c) The light control value should be set on the ground when the natural illumination is 5 Ix-10 Ix;
d) Measures to prevent the light source from being repeatedly turned on and off when the light source is turned on or off.
6.3.3 DC power supply to lighting components should be used. Inverter power supply can also be used.
Inverter power supply, "inverter" should meet the performance of lighting components, power requirements. Should comply with the provisions of GB/T 19064.
6.4 Lighting Components
6.4.1 The safety requirements and performance requirements of electric light sources shall comply with the relevant national standards.
6.4.2 Electric light source accessories
a) DC electronic ballasts shall have constant power output characteristics in addition to the provisions of GB 19510.5 and GB/T 19656;
b) Fluorescent lamps DC electronic ballasts shall comply with the provisions of GB/T 15144, shall have a good warm-up start, filament warm-up start-up time should reach at least 0.4s.
6.4.3 Luminaires
a) The safety performance shall comply with the requirements of GB 7000.1 and GB 7000.5. Protection level should not be lower than IP54;
b) Garden lights should have a reasonable light distribution;
c) The road lighting fixtures should adopt half-cut light distribution, which matches the type and power of the selected light source, and the efficiency of the lamps should not be lower than 70%;
d) LED lamps should meet the requirements of the relevant standards.
6.5 Structural Components
6.5.1 Lamp Post
a) Installation height of lighting fixtures: Lawn lights should be less than 1m, courtyard lights should be 2.5m-4m, road lighting lights should be 4m-8m;
b) The height of the pole should meet the mounting height of the luminaire and the installation requirements of the solar module;
c) The use of hot-dip galvanizing and spray-painted steel pipes for lampposts shall be in compliance with relevant national standards.
6.5.2 After the solar cell holder is combined with the lamp post, it should be able to withstand the wind load specified in 5.3.1.
6.5.3 The controller room shall have waterproof and moisture proof measures. The controller room door should be fixed with a special anti-theft screw and should be easy to maintain.
6.5.4 The battery room shall have functions of waterproof, moisture-proof, anti-corrosion, thermal insulation, heat insulation, ventilation, and protection of the battery from external force. It shall be provided with acid gas to prevent the discharge of the interior of the lamp stem, the controller, the cable and the lamp. Corrosion measures.
6.6 Charge and discharge lines
6.6.1 The section of the conductor shall be greater than 1.5mm2. When the power of the lighting assembly is less than 10W, it shall be greater than 0.5mm2 and shall meet the mechanical strength requirements.
6.6.2 Line Voltage Drop
a) When the solar cell module is charging the battery with the rated current through the controller, the voltage drop between the output end of the solar cell module and the input end of the controller should not exceed 3% of the rated voltage of the battery;
b) When the storage battery discharges the lighting component through the controller at the rated current, the line voltage drop between the output terminal of the battery and the battery input terminal of the controller shall not exceed 1% of the rated voltage of the battery; the output of the controller and the lighting component The pressure drop at the human end should not exceed 3% of the rated voltage of the battery.
7 test methods
Tests are divided into component tests and overall tests. The overall test is passed after the parts are inspected and assembled.
7.1 Component Test
7.1.1 Solar photoelectric conversion device (6.1)
a) The solar cell performance (6.1.1) is tested according to the test methods specified in GB/T 9535, GB/T 11011 and GB/T 18911;
b) The operating voltage of the solar module (6.1.3) is measured with a solar cell outdoor tester.
7.1.2 Battery (6.2)
Tested in accordance with GB/T 19638.2, GB/T 19639.1.
7.1.3 Charge and Discharge Controller (6.3)
a) The performance of the charge-discharge controller (6.3.1) is tested in accordance with 8.2.2-8.2.12 and related standards in GB/T 19064-2003;
b) Ambient temperature test (6.3.2) Place the controller in a thermostatic chamber and perform 10 temperature cycling tests from the lowest to the highest ambient temperature for 4 hours per cycle. After the test, the controller should be able to work normally in the minimum and maximum two ambient temperatures respectively;
c) The inverter (6.3.3) shall be tested in accordance with 8.4.2-8.4.11 of GB/T 19064-2003.
7.1.4 Lighting Components (6.4)
a) The electric light source (6.4.1) shall be tested according to the relevant national standards and shall comply with its requirements;
b) Electric light source accessories (6.4.2) DC electronic ballasts shall be tested in accordance with the methods specified in GB 19510.1, GB 19510.5.GB/T 19656. And should be constant power and fluorescent lamp filament preheating requirements;
c) The safety performance of the luminaire (6.4.3) shall be tested according to the test method specified in GB 7000.1.GB 7000.5;
LED lamps should be tested according to relevant standards.
Optical properties should be tested according to GB/T 9468 regulations.
The optical inspection report should include: polar coordinate light intensity distribution curve, equal light intensity curve, illuminance curve of the road surface, uplit ratio of the luminaire, and lamp efficiency. For road lighting fixtures, light intensity distribution tables, utilization factor curves, etc. should also be included.
7.1.5 Structural Components (6.5)
a) Lamp poles with visual, touch, rulers, calipers and ultrasonic thickness gauge related parameters;
b) The solar cell module holder is measured by visual, touch and ruler measurements;
c) relevant parameters for visual measurement, touch and ruler measurement in the controller room and battery room.
7.2 Overall test
7.2.1 Appearance (5.3.5, 6.5) Visual inspection, ruler measurement, touch test.
7.2.2 Grounding resistance (5.3.3) Measure the resistance of the lamp pole grounding electrode and ground (measured after installation on site) with a grounding resistance meter.
Insulation resistance (5.3.4) Insulation resistance meter measures the insulation resistance between the conductive part and the steel lamp post.
7.2.3 Charge and Discharge Lines (6.6)
7.2.3.1 Conductor cross-section (6.6.1): Inspection with micrometric caliper measurements.
7.2.3.2 Line voltage drop of the device ((6.6.2): ​​check with a 0.5-level DC voltmeter measurement and calculation method:
a) Charging circuit:
The voltage drop from the output end of the solar cell module to the controller's charge input line (6.6.2a)) replaces the solar cell module with an adjustable regulated power supply, and the output end of the solar cell module is connected to an adjustable voltage regulator power supply. The charging input is terminated to an analog adjustable load. Adjust the adjustable regulated power supply voltage to the rated voltage of the solar cell module, adjust the analog adjustable load, make the output current of the solar cell module be the rated current, measure the output voltage of the solar cell module and the input voltage of the controller, calculate two Difference.
b) Discharge circuit:
The voltage drop from the battery output to the controller's battery input and controller outputs to the lighting unit's input to the lighting unit (6.6.2b)) Replace the battery with an adjustable regulated power supply, and terminate the controller's battery input. Adjustable regulated power supply; After the controller has been used to operate the lighting device for 1 h under rated conditions, measure the voltage at the output of the controller and the lighting components (inverter power supply, then with the inverter) input terminal voltage (6.6.2b) ); Battery output and controller input voltage (6.6.2b)), calculate the difference between the two.
7.2.4 Switch Lamp Control (6.3.2)
Light control plus time control: light control turn on the light, use the illuminometer to measure the natural light level value of the ground when turning on the light;
When the lights are turned off, they should be adjusted according to the season and the lighting time should be measured with a timer.
Time control: The time for turning lights on and off should be adjusted according to the season. The lighting time is detected by a timer.
Illumination control: Use the illuminometer to measure the natural illuminance of the ground when the device is turned on or off.
7.2.5 Device Performance (5.2.2)
a) Electrical efficiency (5.2.2a)):
Replace the battery with an adjustable regulated power supply, connect a 0.5-level power meter at the output end and the input end of the lighting component, adjust the output voltage of the adjustable regulated power supply to the rated voltage of the battery, and turn on the lighting through the controller. Components, measuring the ratio of the input power of the lighting component to the output power of the adjustable regulated power supply, and calculating the electrical efficiency;
b) Continuous discharge capacity (5.2.2b)):
If the device continues for n rainy days, the storage capacity of the battery needs to be maintained for n+1 days.
The device shall be in normal lighting for ((n ± 1)) x N hours (N: lighting time for the device per day).
When the battery is fully charged, disconnect the solar module, and inspect the following method to meet the requirements of (5.2.2b)). The depth of discharge of the battery in every N hours is not greater than "80/(n+1)]%. ;
After the last N hours of normal lighting, the battery should have at least 20% of the stored power.
7.2.6 Wind load (5.3.1)
The manufacturer shall provide design calculation instructions for the installation to withstand the wind loads specified in 5.3.1.
8 inspection rules
8.1 Inspection Classification
Inspection is divided into factory inspection and type inspection.
8.2 factory inspection
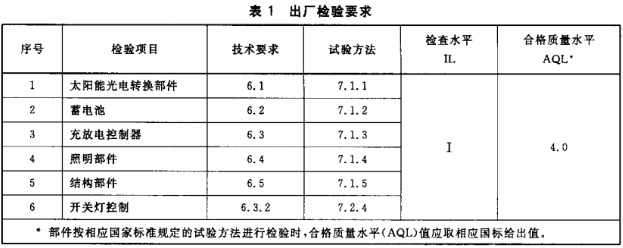
Performed according to the provisions of GB/T 2828.1. With a single sampling, the project, inspection level and quality level of conformity shall be in accordance with Table 1.
8.3 type test
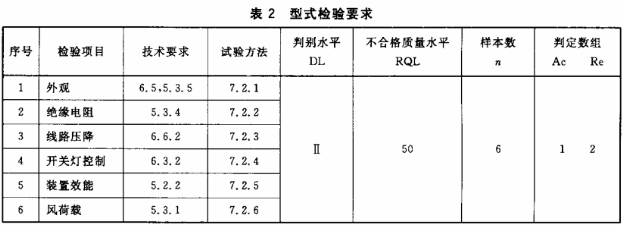
According to the provisions of GB/T 2829 implementation. With a one-time sampling plan, the conditions for the project and passing judgment shall comply with the requirements of Table 2.
Samples are randomly selected from products that have passed the factory inspection.
If the type test fails, the batch is unqualified. The production and acceptance shall be stopped immediately, and the products that have been checked and stopped shall be stopped, the reasons shall be ascertained, and measures shall be taken until the new type inspection is qualified and the production and acceptance can only be resumed.
Type test is not less than once a year. A type test should be performed when one of the following conditions occurs:
a) At the time of product qualification test;
b) Stop production for more than half a year and resume production;
c) when design, process or material changes may affect its performance;
d) When the quality and technical supervision department puts forward the inspection.
9 signs, packaging, transportation and storage
9.1 mark
The device should have the following clear and firm signs:
a) product name, model, trademark;
b) Specifications and models for supporting solar cell modules, batteries, and electric light sources;
c) Manufacturer, date of manufacture, use of standard number.
9.2 Packaging
a) Each part of the device should be packaged separately, and the packaging box should meet the requirements of moisture-proof and shockproof;
b) Outside the box should be "upward", "careful light release", "moisture protection", "stacking layer limit", etc., shall comply with GB/T 191 regulations
c) The packing box should have documents such as parts list, installation instructions, product certification, user manual and maintenance management instructions.
9.3 Transportation
a) The requirements for loading, unloading and transport and the protective conditions during transport should be stated in the conditions of transport and precautions;
b) The rain and snow shall be prevented from attacking and vibrating strongly;
c) The device should be described when it has special transportation needs.
9.4 Storage
The device should be stored in a well-ventilated room with a relative humidity of no more than 8000 and no corrosive gas in the air.
The stock time should not exceed 1 year.
Ball Valve ,Steel Ball Valve,Stainless Steel Ball Valve,1 Inch Ball Valve
Zhejiang Chenxiang import and export trade Co., Ltd , https://www.chenxiang-valve.com