For Chinese solar companies, July 5 is a day worth celebrating. On this day, the National Development and Reform Commission has included the construction of photovoltaic power plants in the western region into the 23 major projects for the start of the western development in 2010.
As the “trial field†of China's photovoltaic industry, the photovoltaic industry in the western region has been developing rapidly in recent years.
Zhao Yuwen, director of the Photovoltaic Committee of the China Renewable Energy Society, told China Business News that China will add at least 500 megawatts of photovoltaic installed capacity this year. By the end of 2009, the country’s installed photovoltaic capacity was only 300 megawatts.
Most of these installed capacity are concentrated in the western region. In the light of the gradual reduction of foreign PV industry subsidies and fierce competition, this is the temptation of the current domestic 60 solar cell manufacturers that cannot resist.
From bright project to energy supply base
The western region began to develop the photovoltaic industry early on, but only to solve the problem of power supply in remote areas.
Since the 1980s, China has begun to promote photovoltaic systems in remote farming and pastoral areas, with a total installed capacity of 420 kilowatts of “Tibetan non-energy resources, non-power photovoltaic power station construction†project, using photovoltaic technology to end seven counties in Tibet. No history of electricity.
In 2008, the country has installed a total installed capacity of about 140 MW. From 2002 to 2004, the National Development and Reform Commission organized and implemented the project of “transmitting electricity to townships†and built nearly 720 solar photovoltaic power stations with a total installed capacity of 19.6 megawatts, which has solved the problem of power supply for all local governments in China.
Before China has truly recognized the importance of photovoltaic power generation, developed countries have developed large-scale photovoltaic power generation. In 2008, the output of photovoltaic cells in China accounted for 31.3% of the world's total, but the installation of photovoltaic systems accounted for 0.71% of the world's total installed capacity (5.6 million kilowatts).
The real start of the domestic market was in 2007 after the National Development and Reform Commission released the "Long-Term Development Plan for Renewable Energy." The specific goal is that by 2010, the installed capacity of solar power in the country will reach 300 megawatts, and by 2020 it will reach 1800 megawatts.
"The large-scale grid-connected power stations are mainly developed in the western region," Shi Dingyi, the counselor of the State Council and chairman of the China Renewable Energy Society, told the newspaper.
Due to the abundant illumination resources in the western region and the high cost of photovoltaic power generation, China began to conduct large-scale photovoltaic grid-connected power stations in the western region. The western photovoltaic industry has gradually increased from the initial supply of local electricity demand to becoming China's new energy power supply base.
The western region is also very optimistic about the photovoltaic power generation industry. In order to stimulate economic growth, provinces and regions do not hesitate to issue preferential policies to actively support the development of large-scale photovoltaic grid-connected power generation projects.
Compete for "first"
Judging from the current PV industry plans announced by various provinces and regions, many western provinces hope to develop their photovoltaic industry as a new pillar industry; at the same time, many projects have been advertised as the country's largest photovoltaic power generation projects.
The Ningxia Shizuishan City strives to achieve a polysilicon production capacity of 20,000 tons within five years, a single crystal silicon production capacity of 1,000 tons, a solar cell film production capacity of 54 million, a solar module production capacity of 100 megawatts, and a solar photovoltaic power station with a total installed capacity of 350 megawatts.
In order to attract photovoltaic companies to invest in the local area, Shizuishan City is studying and formulating such policies as the development and utilization of solar energy, price subsidies for wind power generation, and preferential land use, and implementing fiscal and tax incentives for photovoltaic companies.
Inner Mongolia also actively develops the photovoltaic industry. In order to compete with other provinces and regions, the preferential tax policy for Inner Mongolia is that for the photovoltaic industry based in Inner Mongolia, the domestic-funded enterprises and foreign-invested enterprises whose main business income exceeds 70% of the company’s total income for the year are reduced by 2010. 15% tax rate on corporate income tax.
Both of these major autonomous regions are the regions with the most abundant solar energy resources. According to the size of solar radiation, the country can be roughly divided into five categories. The first category is the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, northern Gansu, northern Ningxia, and southern Xinjiang. This is the region with the most abundant solar energy resources in China; the second category is Northwestern Hebei. Department, northern Shanxi, southern Inner Mongolia, southern Ningxia, central Gansu, eastern Qinghai, southeastern Tibet and other places.
Before 2008, most of China's solar energy industry was concentrated in the eastern region. The Institute of Electrical Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences organized dozens of experts to conduct research on the photovoltaic industry last year and found that since 2008, there have been some changes in the distribution of the photovoltaic industry. In particular, the polysilicon production link has gradually extended to the central and western regions. Polysilicon projects in Inner Mongolia, Qinghai, Ningxia, Hunan and Hubei provinces have all achieved certain production capacities.
“In many areas in the western region, whether or not the conditions are met, we all hope that we will invest in the area.†Insider of LDK Solar Energy Company in Jiangxi told the newspaper.
Go west!
It is not only Seiwe of Jiangxi. In recent years, photovoltaic companies across the country have gradually entered the western region to seize the market; at the same time, many local companies in the west have also joined the investment force of the photovoltaic industry.
Xie Xiaonan, vice president of Wuxi Suntech Power Co., Ltd., told the newspaper that the company will vigorously develop the western photovoltaic power station market.
On April 9th, the National Development and Reform Commission approved the temporary on-grid electricity price of four photovoltaic power generation projects in Ningxia - RMB 1.15/kWh, including the Suntech project. This project plans to build 50 MW, which is the joint investment of Suntech and China Energy Conservation Investment Corporation.
Last year's Dunhuang Photovoltaic Bidding Project was jointly invested by several companies such as Jiangsu Best Solar Energy Technology Co., Ltd.
After Suntech Wuxi and Seiwei Jiangxi took over the western photovoltaic market, other domestic companies are stepping up their development in the west.
"We are planning to develop the market in the western region." Chen Dongbing, deputy chief engineer of the Changzhou Jiaxun Optoelectronics Research Institute under Changzhou Jiaxun Photoelectric System Engineering Co., Ltd., told the newspaper.
Chen Dongbing is a former senior engineer of the Institute of Electrical Engineering of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He is also an expert enjoying special allowances from the State Council and has studied photovoltaics for decades. Last year, he also participated in the "Research and Suggestions on Accelerating the Development of China's Domestic PV Market Incentive Policies and Measures." After retirement, he was taken away by his current company. This company aims to get a share of the photovoltaic market as soon as possible.
Prior to this, Changzhou Jiaxun was only engaged in photovoltaic system engineering in the eastern region, similar to EPC (design, procurement, construction). Last year, the company received a 2 MW solar power project in Anhui.
Disposable serological pipettes with polyester fiber plugs are ideal for tissue culture applications. Crisp, black, highly legible permanent graduations prevent ambiguity and guarantee precise reading and accurate dispensing within ± 2%. Reverse graduations show volume removed or remaining on all pipettes larger than 1mL. Generous negative graduations provide additional pipetting volume. Yongyue's serological pipettes are made from transparent USP Class VI polystyrene sterilized by gamma irradiation. Each lot is free from pyrogens, DNases, and RNases.Yongyue's plastic serological pipettes are produced under the strictest protocols and offer the highest degree of accuracy.
The pipettes are supplied with an aerosol barrier plug that prevents both liquid and aerosols from contaminating the pipettors.
The serological pipettes are produced from crystal clear polystyrene (PS) and are color coded for easy volume identification. Available in 1mL, 2mL, 5mL, 10mL, 25mL and 50mL sizes.
In addition each Pipette now features:
Crisp and bold easy-to-read graduation marks
Reverse graduations on all volumes
Negative graduations on all volumes
1, 2 and 5mL pipettes feature one-piece construction
10, 25 and 50mL pipettes feature three-piece construction
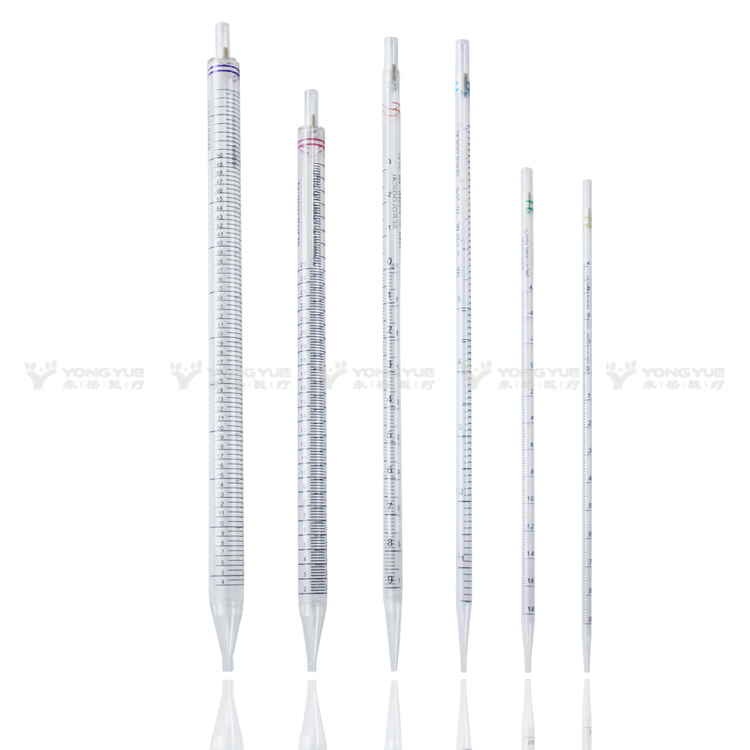
1 ml Serological Pipette,50 ml Serological Pipette,10 ml Serological Pipette,5 ml Serological Pipette,25 ml Serological Pipette,Serological Pipette 2ml
Yong Yue Medical Technology(Kunshan) Co.,Ltd , https://www.yongyuecellculture.com