For the driver of the car, the driving pleasure brought by the manual transmission and the convenience brought by the automatic transmission are a pair of outstanding contradictions, and the dual clutch automatic transmission (DCT) can solve this contradiction. DCT combines the advantages of hydraulic mechanical automatic transmission (AT) and electronically controlled mechanical automatic transmission (AMT), with high transmission efficiency, simple structure, convenient operation, no power interruption and better matching with diesel engine, not only guaranteeing the vehicle. The power and economy, and improved the comfort of the vehicle.
According to the comprehensive research and analysis of OEMs and aftermarkets by relevant institutions, it is estimated that by 2015, DCT's share in the European transmission market will reach 29%; in Asia Pacific (excluding Japan), DCT sales will also grow rapidly. By then, the share can reach 13% (Figure 1).
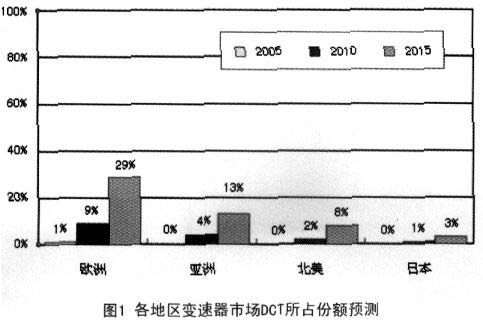
Comparing this data with the situation in 2005 clearly shows that the application of DCT will take a big step in 10 years.
1 Development status of DCT
The concept founding plant of the dual clutch transmission was first introduced in the patent of Kegresses in 1933. After decades of technical improvement, Volkswagen first applied the dual-clutch direct-shift transmission (DSG) to Volkswagen's mass-produced vehicles in 2002 to realize the commercialization of DCT. By the end of 2007, various DSG-equipped cars had sold more than 1 million vehicles.
Features of the main structure of the first generation DSG:
1) 2 wet clutches arranged side by side;
2) 6 forward gears and 1 reverse gear;
3) The gears of the transmission are arranged separately in odd gears (1, 3, 5, R gears) and even gears (2, 4, 6 gears) and are respectively associated with 2 clutches;
4) The output shafts of the two clutches are respectively a solid shaft and a hollow shaft that is placed outside the solid shaft. The two output shafts are concentric, and such a structure makes the transmission more compact.
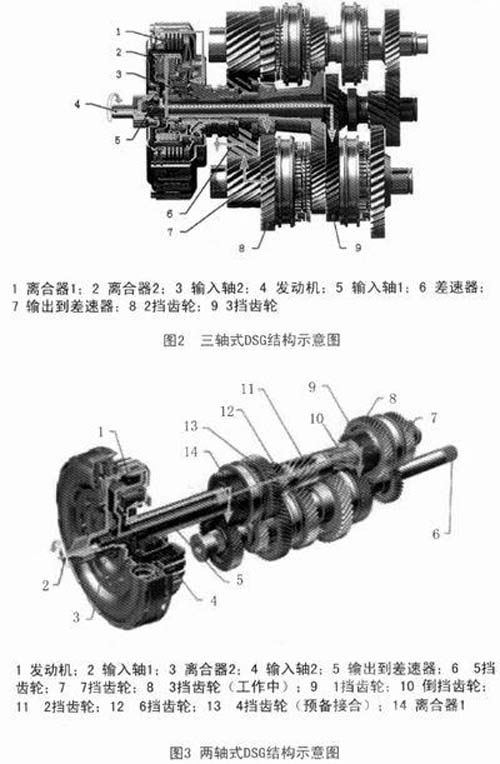
The first generation DSG can be divided into two categories according to the driving form of the vehicle: one is a three-axis DSG (Fig. 2) used in a front-mounted (PF) vehicle such as the Volkswagen Golf GTI, which has a short axial length and is suitable for front-end. Front-wheel drive, but the mechanical structure is more complicated; the other is the two-axis DSG (Fig. 3) used in front-mounted rear-drive (FR) cars such as the Audi Roadjet. The mechanical structure is simpler than the three-axis DSG, but due to the axial length. Longer, only for front-mounted rear-drive cars.
Next page
kaiping aida sanitary ware technology co.,ltd , https://www.aidafaucet.com