The tariffs are overweight and the Sino-US trade war is further escalated. Recently, the United States announced that it will not only impose tariffs on 200 billion US dollars of Chinese goods, but also intends to increase the tax rate from 10% to 25%.
To this end, the Chinese government has also introduced a second round of counter-measures to impose a 5%-25% tariff on US$60 billion.
So, what new changes have this round of trade warfare? What is the overlapping effect of the two rounds of trade wars?

What products are involved in the two rounds of trade war?
The United States has imposed tariff-related goods on China, which has expanded from high-end manufacturing to consumer goods. Specifically, the first round of US $50 billion in taxation is concentrated. The first batch of $36 billion on July 6 includes 1,333 HS eight-digit code sub-items, involving 18 digits of HS two-digit code. The industry is mainly concentrated in high-end manufacturing such as machinery and equipment, electronic equipment, transportation equipment, and pharmaceuticals. This indicates that the first round of taxation is mainly concentrated in high-end manufacturing.
In the second round of taxation, the scale of taxation has increased by 200 billion U.S. dollars from 50 billion U.S. dollars, and the scope of taxation has expanded significantly.
From the list published by the US, the taxation scope covers 6048 HS eight-digit commodities, covering most of the HS double-digit sub-sectors, among which chemicals, textiles and metal products account for the largest number of HS octants, respectively 1435, 932 and 733, accounting for 23.7%, 15.4% and 12.1% respectively, and electromechanical audio-visual equipment continued to reach 416. It can be seen that high-end manufacturing continues to be the main target of the second round of taxation in the United States, and consumer goods such as chemical products, plastic products, and metal products have also entered the scope of taxation.
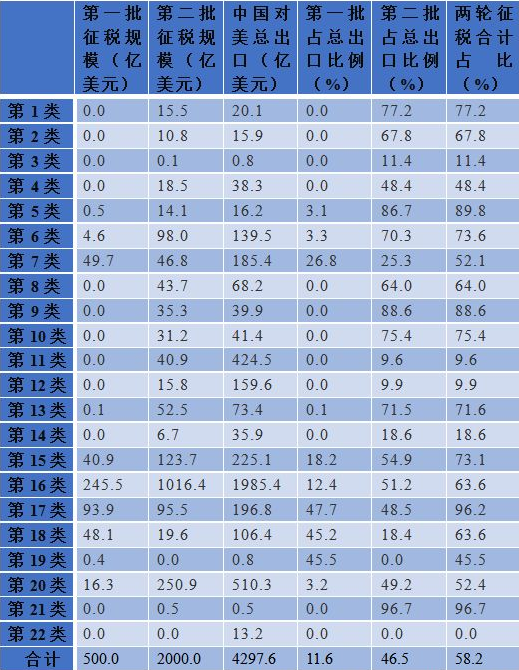

After two rounds of tariffs, the total revenue of electromechanical and audio-visual equipment was US$126.19 billion, which was included in the scope of tariffs imposed by the United States, accounting for 63.6% of China’s exports to the United States. For daily consumer goods, furniture, bedding and lamps were included in the scope of taxation. The export value of miscellaneous products was 26.72 billion US dollars, accounting for 52.4%.
However, it is worth noting that although textiles, clothing, shoes and hats have entered the scope of taxation, they account for no more than 10%. It can be seen that the US imposes tariffs on daily-use consumer goods, which is still selective. It also shows that such goods are still irreplaceable in US imports.
Let’s look at China’s tariff increase on US goods.
On August 3, the Ministry of Finance launched a second round of tariff counter-measures, announcing tariffs on imported goods originating from 5,207 US taxes, totaling $60 billion.
From the list of commodities, China's first round of tax collection list is mainly concentrated in agricultural products, mineral products, etc. The second round of taxation list has expanded to almost all industries. At this point, the increase in tariffs involving imports has accounted for 71.5% of China's imports from the United States, covering most of the tariff items.
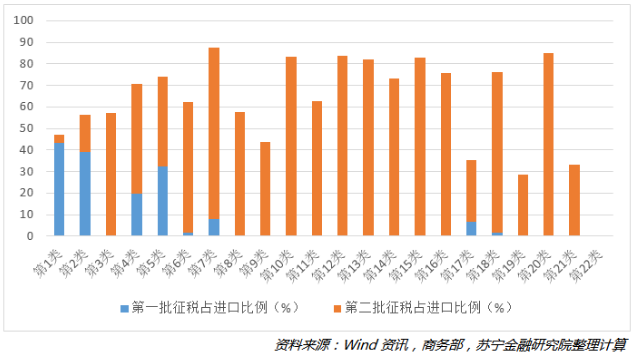
What is the impact of the two rounds of tariff increase after the merger?
First of all, the addition of tariffs will have a certain impact on bilateral trade between China and the United States. In 2017, the bilateral trade volume between China and the United States reached a record high of US$583.7 billion, of which China exported US$429.8 billion to the United States and US$153.9 billion from the United States.
Once the two rounds of tariff policy are fully implemented, it will have a trade transfer effect on both countries, and both countries will seek alternative suppliers from third parties.
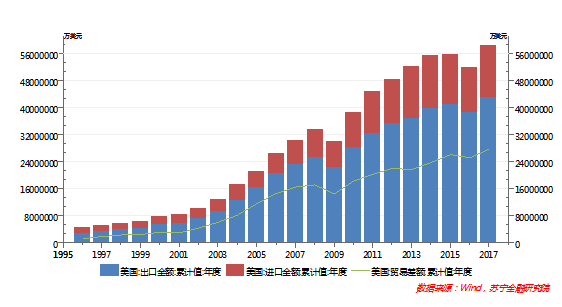
The impact of the addition of tariffs on bilateral trade depends on the price elasticity of the other party's goods.
In terms of China’s exports to the United States, if the tariff is imposed at 25%, China’s exports to the United States will be reduced by 30.9 billion U.S. dollars, and the corresponding export growth rate will slow down by 1.4 percentage points. China’s economic GDP growth rate will also slow down by 0.25. percentage point.
Therefore, China’s exports to the United States are still the most affected by tariffs, such as telecommunications, electromechanical and other high-end manufacturing industries. The impact of labor-intensive industries on US exports is relatively small.
In terms of China’s imports from the United States, China’s tariffs on the United States will increase by 10%, and the overall import value will fall by 7%.
Therefore, the second round of China’s tariff of 5%-25% on US$60 billion of imported goods will result in a contraction of US$6.783 billion, plus a tariff of 25% on the first round of US$50 billion. The resulting reduction of US$8.75 billion, which totaled US$15.533 billion, is equivalent to 0.84% ​​of China’s total imports, and the overall impact is very limited.
Second, the trade war has a greater impact on the inflation of the two countries.
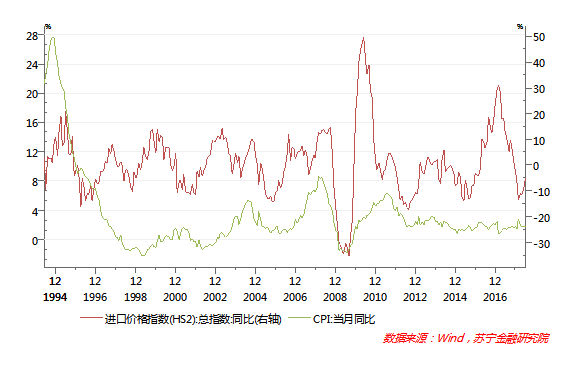
Historical data shows that the US domestic inflation rate is highly correlated with the import commodity price index.
The total US merchandise imports in 2017 was US$ 2,360.8 billion, and the US$ 250 billion in tariff-added goods accounted for 10.5%. If all 25% tariffs are imposed, the import price will be increased by 2.625%.
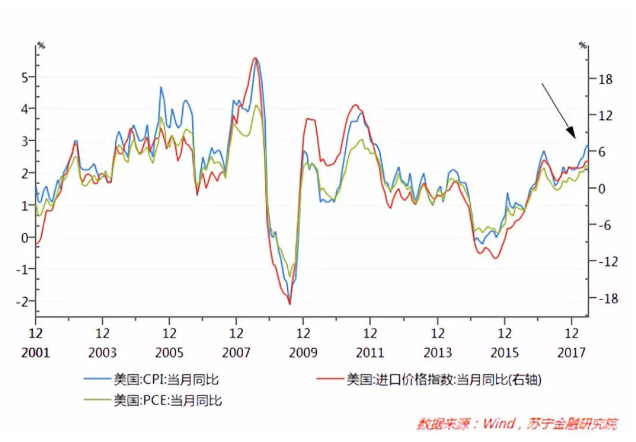
In contrast, China has faced input-type inflationary pressures during the period of high global commodity prices. However, from the long-term historical data, inflation is mainly affected by domestic economic fundamentals, especially pork prices such as food prices, medical services, and rent. The impact is greater, and the correlation with the price fluctuations of imported goods is not significant.
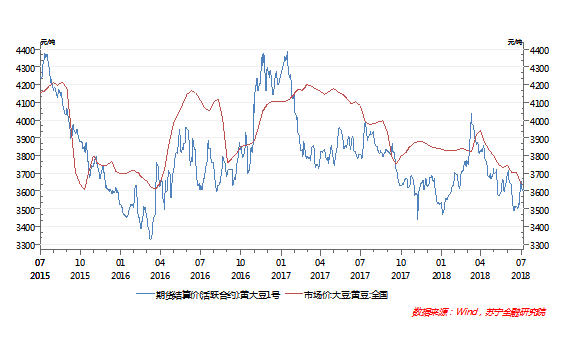
In this Sino-US trade war, the biggest impact on domestic inflation is undoubtedly the possibility of a large upward pressure on domestic soybean import prices.
However, the actual situation may not be so pessimistic, even in the most extreme cases, the national soybean price rose by 25%, driving the CPI rise is only 0.35 percentage points.
On the whole, as far as the trade sector is concerned, although the disputes between the two sides have been further upgraded, the overall impact is still within the controllable range, and the impact on China's exports and economic growth may also be lower than expected.
Of course, China’s impact on high-end manufacturing such as electromechanical and communications will be far greater than that of labor-intensive industries. The domestic economic situation and consumer demand in the United States will be strong, and China’s exports of consumer goods to the United States may even exceed expectations. Of course, all this still needs to see how the Sino-US trade war will evolve next.
Wood Doors ,Solid Wood Exterior Doors,5 Panel Interior Door,Wooden Bifold Doors
Foshan QI'AN Fireproof Shutter Doors Co., Ltd , https://www.fsqianfiredoor.com