Minimize the effect of static electricity on the filter media and at the same time make the media work in an energy efficient manner, which is the main goal of air filtration. Dr. Andreas Seeberger of IREMA FILTER presented some of the latest developments in this article.
It is well known that in air filtration, the basic principles of particle deposition on a filter medium include sieving, inertial collision, direct interception and diffusion. In addition, the use of a suitable synthetic material electrostatic attraction between the particle and the fiber surface can significantly enhance the capture of particles (ie, <1 祄).
Although the effectiveness of these electret filter media is sufficient in many applications, the rationality of its application is still questioned because the electret effect will decay in an unpredictable manner under actual operating conditions. The most obvious impact is the HVAC filtration industry, where the latest test standards for filtration products are required to consider and evaluate the possible charge decay of electret filter media.
At the same time, another factor must be considered, that is, the electrostatic force helps to increase the efficiency of particle removal without increasing the pressure drop of the filter medium. This meets the most important requirement at the moment – ​​the low energy requirements during the use of air filtration products.
Obviously, the use of electrostatic force is a controversial topic.
However, this article will explain how to overcome the shortcomings of electret media by applying a convenient filter media design using microfibers that achieves better energy efficiency and longer life. This article will discuss its two application areas - HVAC filtration and automotive air filtration.
HVAC filtration
Close monitoring of filtration characteristics and efficiency over the life of the filtration industry, particularly in HVAC applications, has been widely accepted and has emerged in the latest test methods. In particular, the long-term stability of the electrostatic charge on the surface of synthetic fibers has been closely observed for decades, because in some cases the effect of surface charge decays over time.
Recently, two of the most commonly used test standards for HVAC filters have been issued, namely the revised ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers) standard 52.2 (with Appendix J) and the European standard FprEN 779:2010, which includes static electricity. The study affects the efficiency of filtration. Different processing methods are used to simulate the discharge effect, charge decay effect, or charge coverage effect in actual work. ASHRAE tends to use ultrafine particles (sub-0.1 micron KCl aerosol) for filter media treatment, while European standards recommend isopropanol treatment (IPA). Although the treatment method itself is still a topic of discussion, the basic principles of its application are now widely accepted by industry insiders, and manufacturers of synthetic filter media must take measures to respond positively to meet the higher mechanical filtration proposed by current test standards. Efficiency requirements.
Higher mechanical efficiencies can be easily achieved by applying a media design that increases airflow resistance. However, this method is not competitive, especially when considering energy consumption. In recent years, the technology for efficient production of submicron fibers and nanofibers has progressed, promoting the production of new synthetic filter media and increasing the mechanical and electrostatic forces used to retain particles. At the same time, the microfibers ensure that the pressure drop of the filter media is maintained at a relatively low level.
IREMA FILTER has developed a new synthetic product for HVAC filtration using its proprietary integrated nanofiber technology. A medium (flat and folded) was tested in a separate laboratory to directly compare the effects of the three different discharge methods below.
â—†Isopropanol (prEN779:2010)
â—†Superfine KCl (ASHRAE 52.2 Appendix J)
â—†Soot nanoparticle
In addition to the EN779 and ASHRAE tests, soot nanoparticles were also used to test the filter media, as the discharge effect of soot has been demonstrated in ASHRAE research projects 1189 and 1190. The reason for this problem is that soot particles are common in urban environments around the world, and they are emitted by two- or four-wheeled vehicles driven by diesel engines.
The filter media consists of polypropylene - a polymer with a distinct electret effect. The depth filter media design consists of multiple zones that meet different filter media requirements such as pleating, dust holding capacity, fine grain retention, and nanofiber protection. The mechanical efficiency of the media depends primarily on the area of ​​the microfibres (as shown in Figure 1).
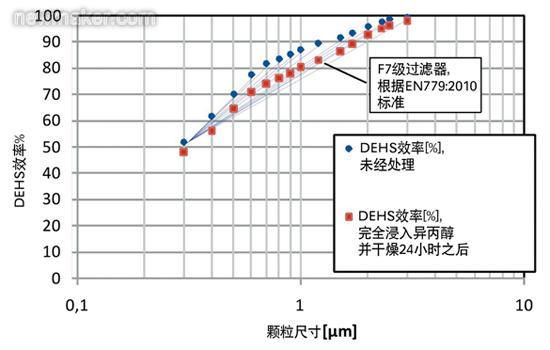
Isopropyl alcohol treatment (prEN779: 2010)
The material was folded separately and tested for its effect on electrostatic forces. The results show that when the conventional EN 779:2002 standard (this is a test without any discharge treatment) is applied, an F7 grade filter will be obtained. EN779:2010 also requires a minimum DEHS particle efficiency of 35% after IPA treatment, which is also met by new filter media. After this, the pleated filter was completely immersed in isopropanol to be uniformly discharged, and then tested again after a drying period of 24 hours in accordance with the requirements of EN779. The strong influence of nanofibers (as small as 0.4 microns in diameter) on mechanical filtration efficiency is evident. The efficiency of a fully-discharged filter decreases very little compared to an untreated sample (as shown in Figure 2). Under similar pressure drop conditions, both test types (untreated and treated) gave an F7 grade filter.
Ultra-fine KCI processing (ASHRAE 52.2 Appendix J)
In stark contrast to EN799's immersion technology is the ASHRAE discharge test, which tends to use a particle-based approach. Ultrafine potassium chloride particles (approximately 40 nm in diameter) were stacked on a pleated filter. At the same time, the removal efficiency of KCl (between 0.3 and 10 microns) was continuously tested until the minimum efficiency was reported. No increase in pressure drop was observed during this adjustment step.
After this, the dust was loaded according to the usual ASHRAE 52.2 test standard to determine the respective Merv classification. With this discharge method, the filtration efficiency of the filter to be tested for small particles is remarkably lowered. This indicates that the surface charge remaining on the fibers has become inactive due to collision with KCl nanoparticles.
However, after applying the full test method, the filter rating is set to Merv 13-A. This means that Merv13 is achieved under discharge conditions (equivalent to European F7), see Figure 3.

Soot nanoparticles
In an urban environment, there are a large number of cars that use diesel engines or other combustion processes, so a large amount of soot nanoparticles and agglomerates are discharged into the surrounding air. At the same time, it is well known that soot particles are a conductive material - often having a large effect on electrostatically charged air filters due to the elimination of the electret effect.
To investigate a second particle-based filter treatment method in addition to the ASHRAE adjustment procedure, soot nanoparticles (average diameter 70 nm) were generated and loaded onto the filter media. The NaCl removal efficiency was continuously measured during loading of the particles. In contrast to the effect of loading KCl nanoparticles, the pressure drop of the filter continues to increase as the soot forms a dendritic structure on the surface of the fiber (as shown in Figure 4).

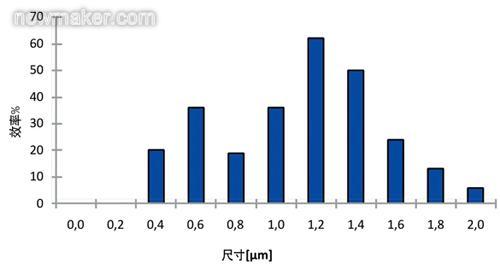
When the particle size is larger than 0.3 μm, the soot particles do not cause a loss of NaCl efficiency at all. A slight decrease in efficiency was observed by applying the SMPS method only under conditions of smaller particle size. Figure 5 shows the initial and minimum efficiency curves (at +50 Pa).

Discussion of the discharge step
Recently, different discharge methods for a special filter medium have been studied and directly compared to determine the electrostatic properties of synthetic fine dust media with integrated nanofibers produced by IREMA FILTER.
The immersion in isopropanol treatment has no significant effect on the removal of DEHS from the gas stream, as required by the latest test standard prEN779:2010. This test method is easy to adopt and the test results are reproducible for flat materials and folding filters of different heights.
If the ASHRAE 52.2 Annex J test method is used, the KCl efficiency is initially high, then drops during the discharge, and the surface charge is detected. The minimum KCl removal efficiency after adjustment is slightly lower than the DEHS removal efficiency after IPA treatment, but the overall range is close. The ASHRAE test method can be repeated at different filter heights, but is difficult to implement because the preparation and characterization of experimental equipment for adjusting aerosols is very rare. In addition, it takes a few days to adjust all the filters, which is expensive. Moreover, even for non-electret media, the variability of this adjustment step in different US laboratories is considerable.
The soot nanoparticles emitted during the combustion process do not actually cause a decrease in the removal efficiency of the NaCl particles. During the loading of the particles, it was found that the pressure drop increased rather rapidly because of the formation of a dendritic structure while also improving the filtration efficiency.
Tests have shown that when nanofibers are used with polypropylene filter media (there is at least an inherent surface charge on the fibers of the material), the effects of surface charge and electret effects are minimized. This means that the synthetic filter material provides the same mechanical efficiency as the fiberglass media, as well as the superior properties of the composite itself, including higher mechanical stability, moisture resistance, or adhesive-free design and flammability.
energy efficiency
Without changing the design of the medium, higher mechanical filtration efficiency often leads to an increase in air flow resistance and a lower dust holding capacity. Naturally, it will have an adverse effect on energy efficiency.
When microfibers and nanofibers are used, the pressure drop of the filter medium is relatively increased in order to achieve high mechanical filtration efficiency. At the same time, due to the reasonable layout, different fiber diameters optimize the advanced design of the filter media and significantly increase the dust holding capacity. IREMA Fine Dust Filtration Media contains a highly advanced ingredient designed to provide a longer lasting life than traditional fine dust filter media under high mechanical efficiency. The results of the dust loading test of the pleated filter according to the EN779 standard are shown in Fig. 6.

Starting from the same initial pressure drop, IREMA FILTER nanofiber media can hold dust equivalent to twice the dust holding capacity of traditional fiberglass or synthetic fibers. Significant energy savings have been achieved because of the low pressure drop that can be maintained for long periods of time. To estimate the energy requirements of a pleated filter, the following formula can be used:
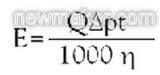
Where E = energy demand [kWh]
Q = flow rate [m3s-1]
ΔP = pressure drop [Pa]
t=time[h]
η = fan efficiency
Typical assumptions:
Dust concentration: 1g Ashrae / day
Flow rate: 3400 cubic meters / second
Energy cost: 0.15 EUR / kWh
Cost per filter: 60 Euro / filter
Labor cost: 15 Euro / shift
Under these assumptions, the IREMA FILTER nanofiber media saves about 14% of energy per year compared to traditional synthetic microfibrous media, and the labor cost savings are saved, saving nearly 20% of total annual cost.
in conclusion
The electret effect is often used to provide high initial efficiency and low pressure drop to synthetic fiber media, a very popular way to use filters with low energy consumption. However, since it is now required to have a high mechanical filtration efficiency after the discharge step, many synthetic fiber media cannot simultaneously satisfy the requirements of both high mechanical efficiency and long service life.
IREMA FILTER uses two methods to meet these requirements:
â—† Use integrated nanofibers for high mechanical efficiency.
â—† Provides extremely advanced media design for higher dust holding capacity.
This approach achieves a perfect combination of high mechanical filtration efficiency and low energy consumption. (end)
The content of the article is for reference only (submission) (If you are the author of this article, please click here) (2012-9-24, read 0 times)
See more air filter related articles: more
·Why clean room should use the junior high-efficiency air filter three-stage filtration system KLCFILTER (2011-8-22)
·Inorganic acid chemical filter knowledge introduction newmaker (2011-3-10)
·Air filter unit conversion newmaker (2011-3-10)
·The terminology of air filter explains newmaker (2011-3-10)
·Air filter selection experience newmaker (2011-3-10)
·Air filter test method and filtration efficiency newmaker (2011-3-10)
·Air filter common sense newmaker (2011-3-10)
· Nanofiber coating technology John Wertz of Hollingsworth & Vose (2010-8-8)
· Is the air filter recyclable? Big 4 Filtration Robert Hall (2010-8-6)
·The filter can be replaced safely with the new filter from Germany Skan (2009-11-25)
See more dryer/air purification/air conditioning related articles:more
·The current hot issues of clean room technology application newmaker (2012-9-21)
·The actual test effect and comparison of NICOLER dynamic air disinfection machine Shanghai Kangjiu Disinfection Technology Co., Ltd. (2012-9-20)
·Control solution for high-power ice storage central air conditioning system newmaker (2012-7-18)
· OMRON technology based LCD workshop clean room air conditioning remote monitoring newmaker (2012-7-18)
·Dehumidification type Hangzhou Lijing (2012-4-7)
·Modbus to Profibus-DP Gateway PM-160 applied to Shanghai Expo Center Shanghai Zibo Automation (2011-12-10)
·Design and implementation of remote monitoring of air conditioning system in intelligent buildings Wang Yiping, Anhui Institute of Architecture and Industry (2011-11-14)
·BMW Welt – an unparalleled experience in B&R Industrial Automation (2011-11-14)
·Spinning plant air conditioning system solutions and energy saving analysis newmaker (2011-11-3)
·Use high power heaters, keep in mind newmaker (2011-10-9)

Concerned about surprises
Label: filter media surface charge fine dust attenuation effect KCI
Previous: Board based on LS-DYNA and FLUENT Next: Effective separation of gas-liquid mixture
Ppgi Coils,Color Coated Sheet,Galvanized Steel Coil
Prepainted Coil Co., Ltd. , http://www.sdhfgroup.com